Rust in Turf
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
Collapse ▲Symptoms
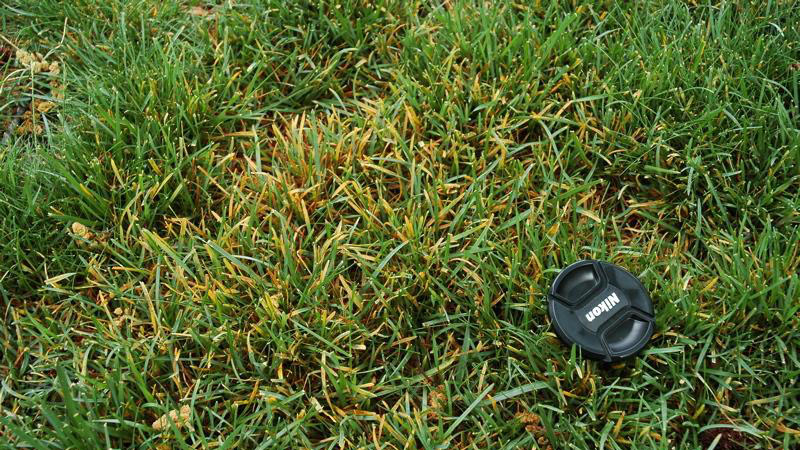
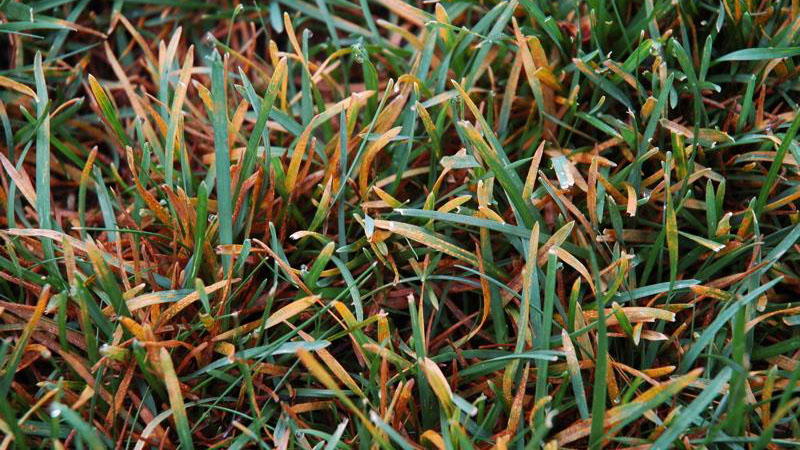
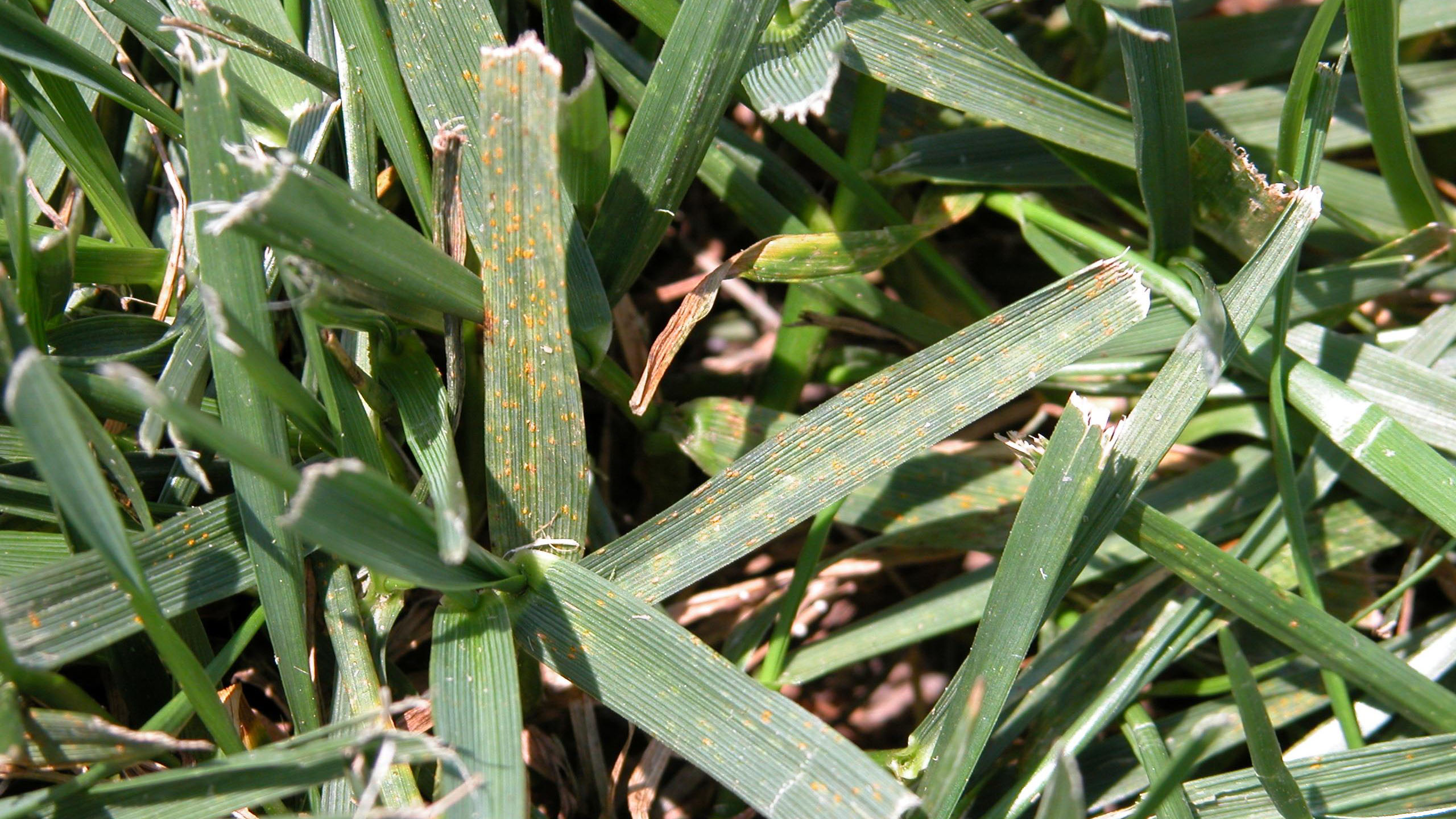
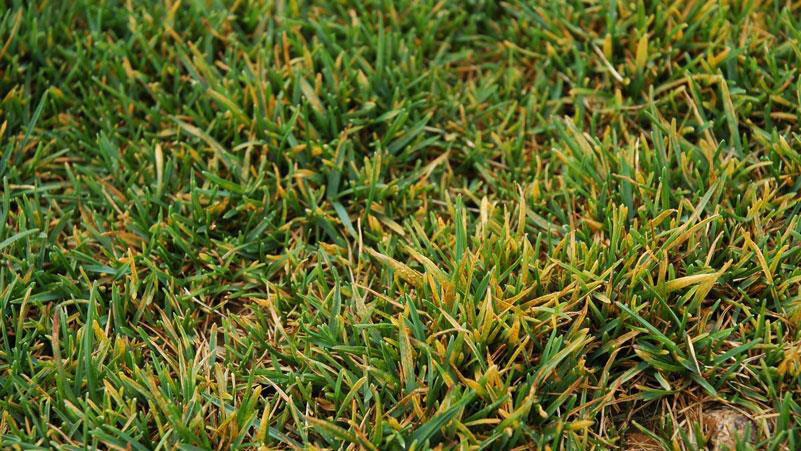
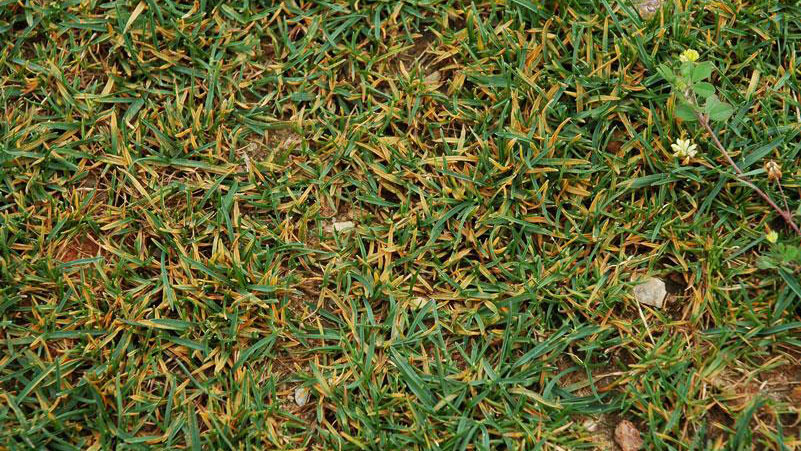
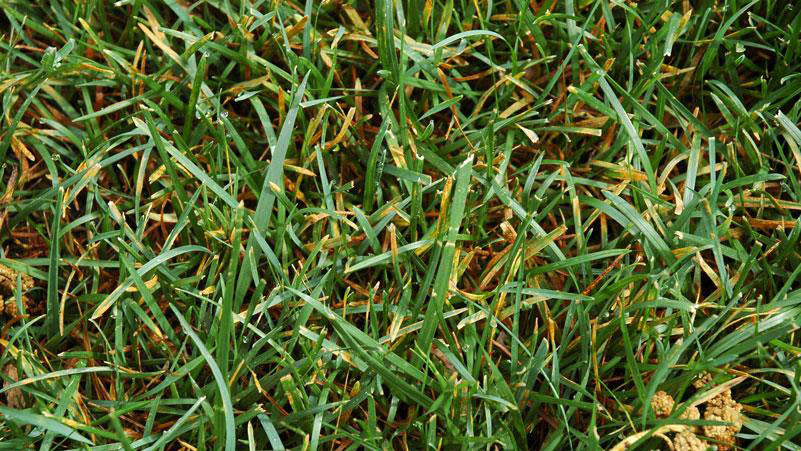
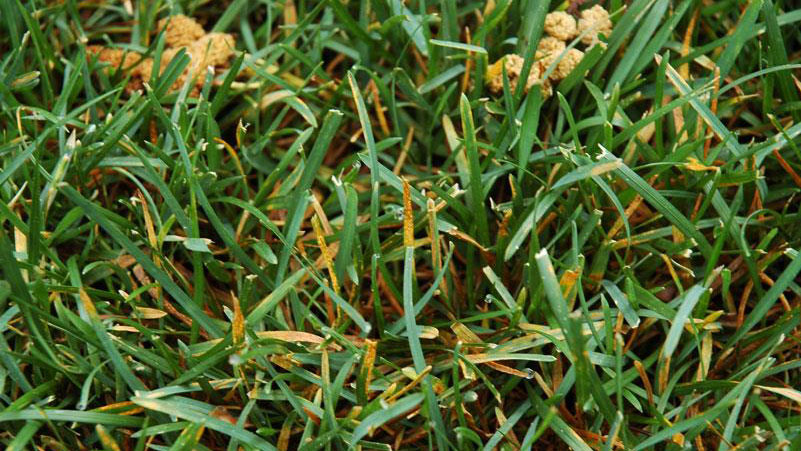
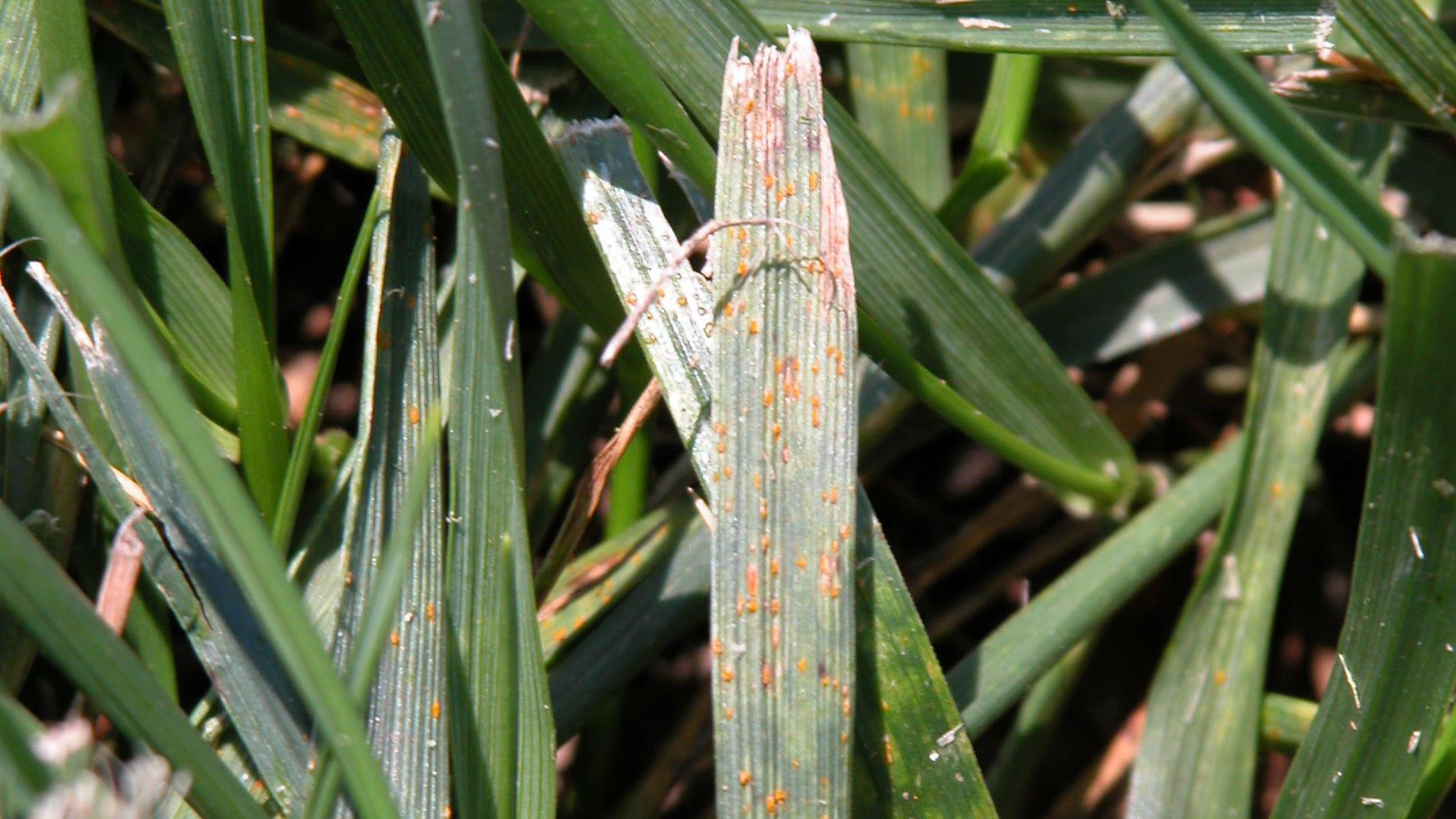
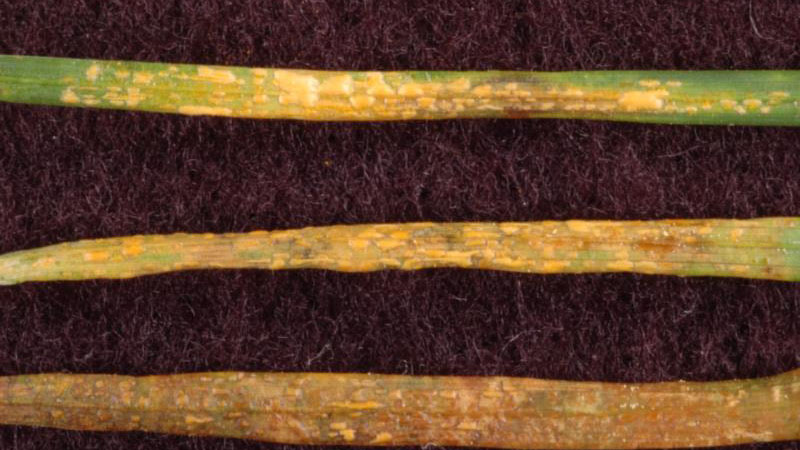
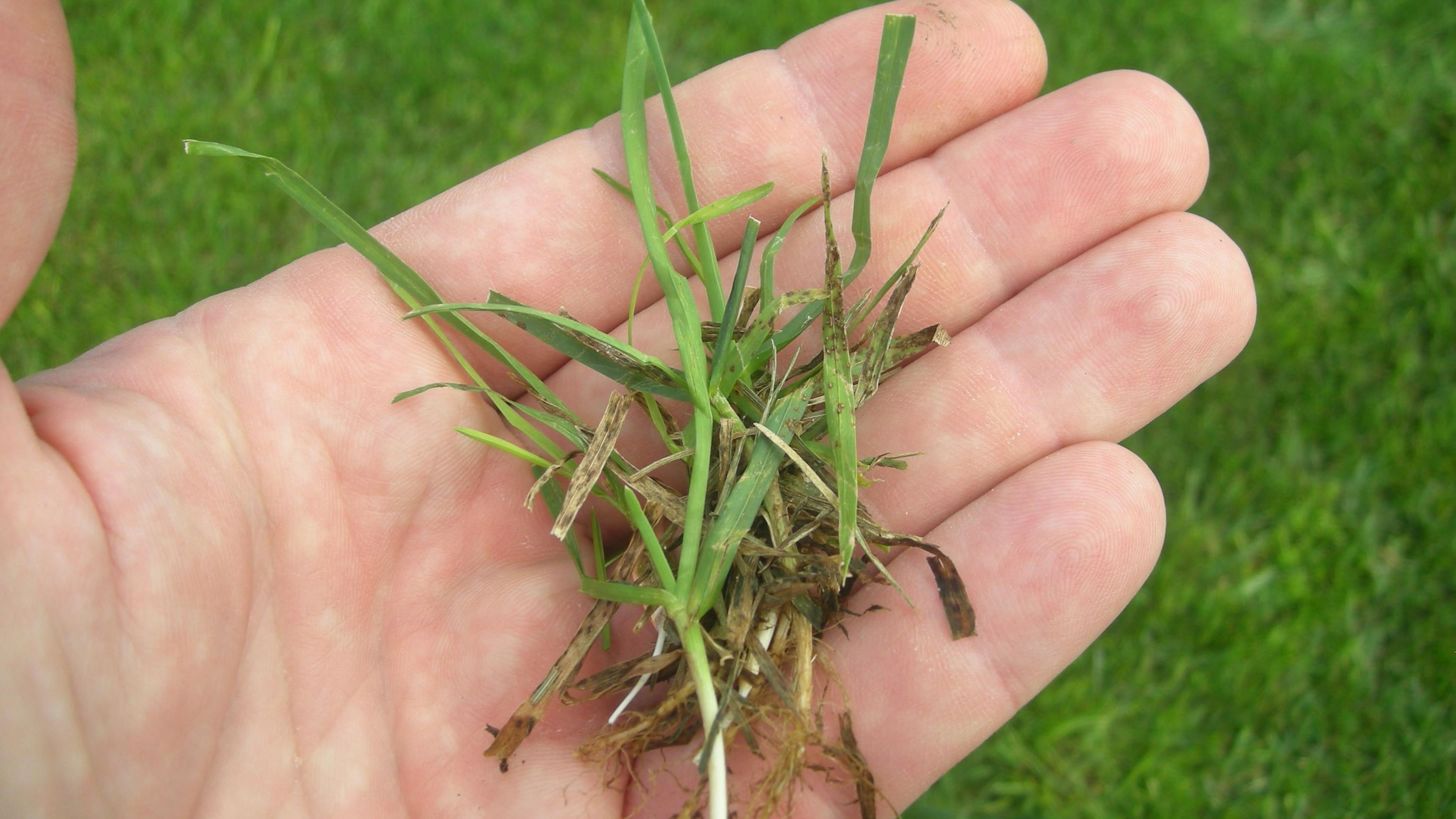
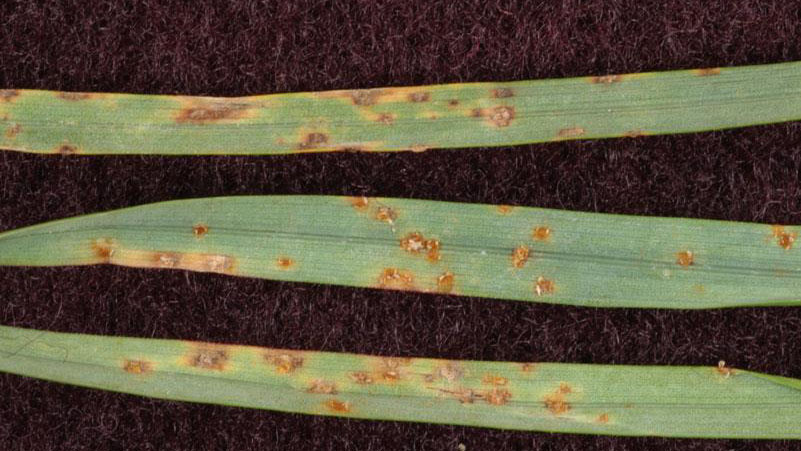
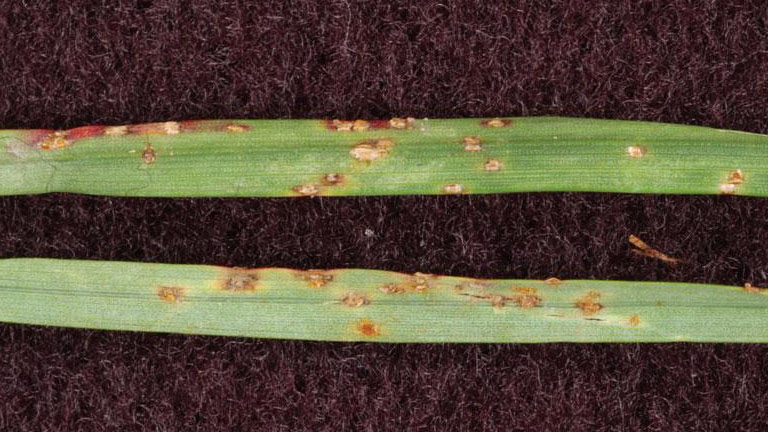
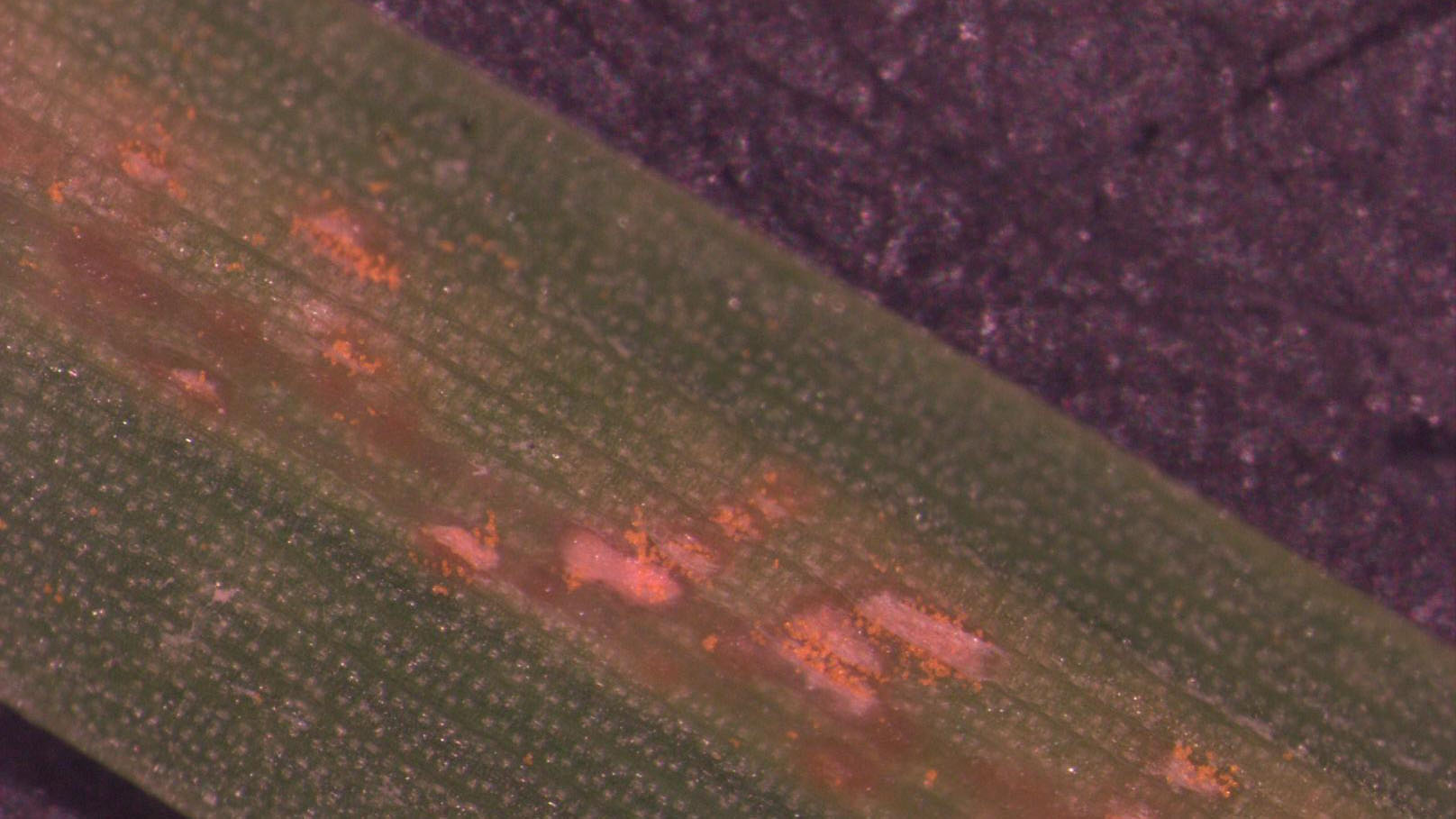
Early symptoms include small, yellow flecks that develop on the leaves and stems. The flecks expand over time into raised pustules, yellow or orange in color, that rupture to release powdery masses of spores. Infected plants become yellow and are more susceptible to environmental stress. Heavily infected areas become thin and exhibit clouds of orange dust (rust spores) when the foliage is disturbed. The rust pustules on infected leaves turn black during the fall in preparation for overwintering.
Development Factors
Rust fungi survive the winter in living plant tissue from which new spores are produced in the spring. Spores produced in the spring, summer, and fall are spread by the wind, germinate on the leaves, and infect new tissue. Extended periods of leaf wetness are required for the spores to germinate and for the disease to develop rapidly.
Rust diseases are most severe in turf that is growing slowly due to adverse weather conditions or inadequate management. Low light intensity, inadequate fertilization, drought stress, and infrequent mowing encourage rust development.
Cultural Control
Plant rust-resistant turfgrass varieties whenever possible to reduce injury from this disease. Select cultivars based on regional trials and university recommendations. When planting cool-season turfs, use blends and mixtures of multiple species and/or varieties whenever possible. Plant shade tolerant grasses and raise mowing heights in heavily shaded areas.
Prune trees and remove unwanted undergrowth to improve air movement and reduce prolonged leaf wetness. Mow the turf on a regular basis, removing no more than 1/3 of the foliage in one mowing. Collect and dispose of clippings taken from infected areas to slow the spread of rust.
Fertilize to meet the nutritional needs of the turf. Submit a soil sample for analysis on a regular basis and apply recommended amounts of phosphorus, potassium, and lime. Apply nitrogen based on university recommendations.
Water deeply but infrequently to encourage deep rooting and reduce drought stress and extended periods of leaf wetness. Avoid watering the turf before sunset or after sunrise.
Chemical Control
Fungicides can be used on a preventative or curative basis for rust control. Susceptible turfs should be monitored regularly for rust development during periods of cool and cloudy weather.
* Products marked with an asterisk are not labeled for home lawn use.
| Fungicide and Formulation1 | Amount of Formulation2 | Application Interval (Days)3 | Efficacy Rating | Resistance Risk | FRAC Code4 |
| azoxystrobin (Heritage) WG TL G |
0.2 to 0.4 1 to 2 2 to 4 lbs |
14 to 28 14 to 28 14 to 28 |
++++ | High | 11 |
| azoxystrobin + acibenzolar-S-methyl (Heritage Action)* | 0.2 to 0.4 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 11/P01 |
| azoxystrobin + chlorothalonil (Renown)* | 2.5 to 4.5 | 14 to 21 | ++++ | High | 11/M5 |
| azoxystrobin + difenoconazole (Briskway)* | 0.5 to 1.2 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 11/3 |
| azoxystrobin + propiconazole (Headway) EC G |
1.5 to 3 2 to 4 lbs |
14 to 28 14 to 28 |
++++ | High | 11/3 |
| azoxystrobin + propiconazole (Compendium) | 1.3 to 2.6 | 14 to 18 | ++++ | High | 11/3 |
| azoxystrobin + tebuconazole (Strobe T)* | 0.75 to 1.5 | 14 to 21 | ++++ | High | 11/3 |
|
benzovindiflupyr + difenoconazole (Ascernity)* |
1.0 | 14 to 21 | ? | ? | 7/3 |
|
boscalid + chlorothalonil (Encartis)* |
4 | 14 | +++ | Medium | 7/M5 |
| chlorothalonil (Daconil Ultrex)* |
3.7 to 5 |
14 | +++ | Low | M5 |
| chlorothalonil (Daconil Weather Stik)* | 4 to 5.5 | 14 | +++ | Low | M5 |
| chlorothalonil (Daconil Zn)* | 6 to 8 | 14 | +++ | Low | M5 |
| chlorothalonil + acibenzolar-S-methyl (Daconil Action) * | 4 to 5.4 | 14 | +++ | Low | M5/P01 |
| chlorothalonil + fluoxastrobin (Fame C)* | 3 to 5.9 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | M5/11 |
| chlorothalonil + propiconazole (Concert II)* | 4.5 to 8.3 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | M5/3 |
| chlorothalonil + propiconazole + fludioxonil (Instrata)* | 2.75 to 6 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | M5/3/12 |
| chlorothalonil + thiophanate-methyl (Spectro)* | 3.72 to 5.76 | 7 to 14 | +++ | Medium | M5/1 |
|
cyazofamid + azoxystrobin (Union) |
2.9 to 5.75 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 21/11 |
|
fluindapyr + flutriafol (Kalida) |
0.25 to 0.4 | 14 to 21 | +++ | Medium | 7/3 |
| fluoxastrobin (Fame) | 0.18 to 0.36 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 11 |
| flutriafol (Rayora)* | 0.7 to 1.4 | 14 to 21 | ++++ | Medium | 3 |
| mancozeb (Fore)* (Dithane)* |
4 4 |
|
++ | Low | M3 |
| metconazole (Tourney) | 0.37 | 14 | ++++ | Medium | 3 |
| myclobutanil (Eagle) | 1.2 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | 3 |
| propiconazole (Banner MAXX II) | 1 to 2 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | 3 |
|
pydiflumetofen + azoxystrobin + propiconazole (Posterity XT)* |
1.5 to 3 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 7/11/3 |
| pyraclostrobin (Insignia) WG SC |
0.5 to 0.9 0.4 to 0.7 |
14 to 28 14 to 28 |
++++ | High | 11 |
| pyraclostrobin + boscalid (Honor)* | 0.55 to 1.1 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 11/7 |
| pyraclostrobin + fluxapyroxad (Lexicon Intrinsic) | 0.34 to 0.47 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | High | 11/7 |
| tebuconazole (Torque)* (Mirage)* |
0.6 to 1.1 1 to 2 |
21 14 to 28 |
++++ | Medium | 3 |
| triadimefon (Bayleton) | 0.5 to 1 | 15 to 30 | ++++ | Medium | 3 |
| trifloxystrobin (Compass) | 0.1 to 0.15 0.2 to 0.25 |
14 21 |
++ | High | 11 |
| trifloxystrobin + triadimefon (Armada) (Tartan)* |
0.6 to 1.5 1 to 2 |
14 to 28 14 to 28 |
++++ | High | 11/3 |
| triticonazole (Trinity) (Triton) |
0.5 to 1 0.28 to 0.55 |
14 to 28 14 to 28 |
++++ | Medium | 3 |
| triticonazole + chlorothalonil (Reserve)* | 3.2 to 4.5 | 14 to 28 | ++++ | Medium | 3/M5 |
| 1 Other trade names with the same active ingredients are labeled for use on turfgrasses and can be used according to label directions. 2 Units are oz, fl oz, or lb depending on formulation. Apply fungicides in 2 to 5 gallons of water per 1,000 square feet according to label directions. Use lower rates for preventive and higher rates for curative applications. 3 Use shorter intervals when conditions are very favorable for disease. 4 Fungicide Resistance Action Committee code. Products with same code have the same mode of action and are in the same chemical class. * Products marked with an asterisk are not labeled for home lawn use. |
|||||
| Efficacy Rating ++++ = excellent control when conditions are highly favorable for disease development +++ = good control when disease pressure is high, excellent control when disease pressure is moderate ++ = good control when disease pressure is moderate, excellent control when disease pressure is low + = good control when disease pressure is low ? = not rated due to insufficient data |
|||||
| Resistance Risk Low = Rotate to different chemical class after 3-4 applications; tank mixing not necessary Medium = Rotate to different chemical class after 1-2 applications; tank-mixing with low or medium risk product recommended High = Rotate to different chemical class after EVERY application; tank-mix with low or medium risk product for EVERY application ? = not rated due to insufficient data |
|||||
Species Data
- HOST SPECIES
- MONTHS WITH SYMPTOMS
- March to June, September to November
- STAND SYMPTOMS
- FOLIAR SYMPTOMS LOCATION / SHAPE
- dieback from leaf tip, blighting of entire leaves, or no distinct leaf symptoms
- FOLIAR SYMPTOMS COLOR
- ROOT / CROWN SYMPTOMS
- none
- FUNGAL SIGNS
- blisters on leaves